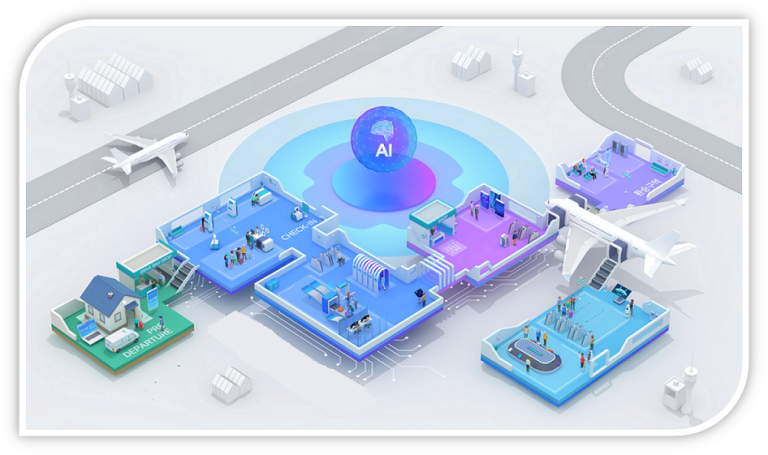
رشد سریع مسافران و افزایش تقاضا ممکن است برخی فرآیندهای حیاتی در ترمینال فرودگاه از جمله پذیرش، سیستمهای یکپارچه، CUTE و سیستمهای عامل را با محدودیتهایی مواجه نماید. از این رو، بسیاری از فرودگاهها در سراسر جهان کاملاً مجهز به فناوریهای مدرن بوده و آماده تحول دیجیتال هستند. در چنین فرودگاههایی از نوآوریهای پیشرفته در فناوری اطلاعات و مخابرات استفاده میشود. به سطح انطباق یک فرودگاه با فناوری “بلوغ دیجیتال” میگویند که میتوان آن را به چهار مرحله تقسیم کرد: فرودگاه 1.0، 2.0، 3.0 و 4.0.

بر این اساس، فرودگاههای سنتی که دارای فرآیندهای دستی هستند و از راهحلهای پایه برای فناوری اطلاعات استفاده مینمایند به عنوان فرودگاه 1.0 شناخته میشوند. سطح بعدی، یعنی فرودگاه 2.0 از فناوریهای مدرن اولیه و تسهیلات self-service جزئی مانند فناوری Wi-Fi و پذیرش دیجیتال استفاده میکنند. فرودگاه 3.0 به فرودگاهی گفته میشود که تمام سطوح خدمات مسافری آن به صورت self-service ارائه میشود. در چنین فرودگاههایی بخشهای کنترل و عملیات خودکار هستند و به طور مرتب از راهحلهای پیشبینیکننده استفاده میشود.
فرودگاههای 4.0 یا هوشمند از دادههای کلان و دادههای باز برای ارتقای نوآوری استفاده مینمایند. اپراتورها در این فرودگاهها به طور مداوم دادهها را در زمان واقعی جمعآوری نموده و پروفایل مسافران را تجزیه و تحلیل میکنند. کارایی عملیاتی در این فرودگاهها نیز با یک مقدار مشخص ارزیابی میشود. از طرف دیگر، اینترنت اشیاء امکاناتی را برای تعامل با دستگاههای هوشمند مختلف فراهم کرده و به بهبود زمینههای مختلف مانند محیطزیست، امنیت، شهرهای هوشمند و صنعت کمک میکند.

فرودگاههای هوشمند تمایل به تنظیم مجدد فرآیندهای خدماتی با اینترنت اشیاء، شبکه تلفن همراه و داده کلان دارند. برخی از پژوهشگران این مفهوم را به عنوان یک راه حل فرودگاهی با قابلیت کنترل از راه دور سیستمهای مختلف تعریف میکنند که علاوه بر فراهم کردن محیطی امنتر برای مسافران باعث رسیدگی فوری به مشکلات خواهد شد.
امنیت
راحتی مسافر
کارایی عملیاتی
بهینه سازی منابع محدود
Smart Airport
The rapid growth of air passengers has put an immense amount of pressure on critical airport processes and has limited the efficiency of check-in, integrated systems, CUTE (Common User Terminal Equipment) and “Agent-facing” systems which shared with regulatory agencies and concessionaries. Hence, many airports worldwide are well equipped with modern technology and are ready for digital transformation. The level in which airports are adapted to technology is known as the digital maturity. This can further be further divided into four stages such as Airport 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 4.0.
Based on this classification, the traditional airports which use manual processes and have basic information technology solutions are called Airport 1.0. on the other hand, Airport 2.0 integrates early digital technology into airport operations and uses partial selfservice facilities including Wi-Fi & automatic check-in and so on. The third level is known as airport 3.0 and it is defined by its full self-service technology. These airports are heavily dependent on predictive solutions and have automated operations.

Airports 4.0 or smart airports apply big data and open data to their services in order to enhance their own innovation. In these airports, Operators continuously collect real-time data and analyze passenger profiles. Operational efficiency is also constantly evaluated with specific criteria. furthermore, by using the state of the art technologies such as The Internet of Things, airport 4.0 are able to improve various airport domains such as environment, security, and industry
Smart Airports tend to reset their service process according to recent technological advances including IoT, mobile network and big data. According to research, unlike traditional airports, “smart and digital” concept is an airport solution which gives the operators the ability to control and monitor systems from a remote area. The advantages of this solution include providing a safer environment for passengers and personnel and detecting and handling errors or faults immediately.
Convenience
Security